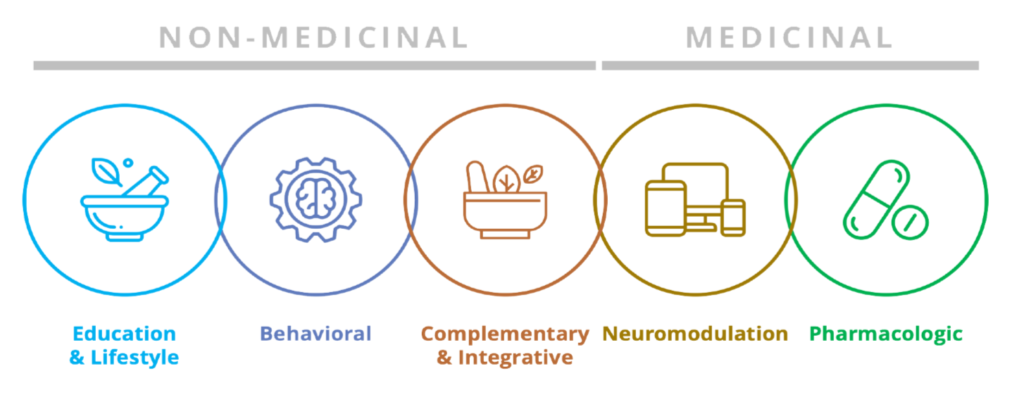
Non-Medical Migraine Treatments
We recommend you read the Quick Start guide before using this directory.
This section includes a wide variety of alternative, complementary, natural, and holistic treatments. They are categorized as Therapy, Behavioral Therapy, Physical Therapy, Product/Device, Procedure, Lifestyle and Vitamin/Supplement.
Although these are nondrug related treatments and generally nonprescription, they should be discussed with your doctor as part of your total treatment plan.
How to use this reference:
- Nonmedical Treatment: The therapy/vitamin/lifestyle practice/device/procedure being used i.e. Acupuncture.
- Treatment Type: Acute treatments are taken at the onset of a migraine attack to help treat the symptoms of pain, nausea or other migraine- related disability. Preventive treatments help reduce or stop migraine attacks from occurring in the first place. Preventive treatments are often taken regularly (i.e. daily, weekly, monthly) whether or not you have a migraine attack.
- Cost: Is the treatment free to perform or does it involve a paid cost? Acupuncture involves a cost to see an acupuncturist.
- Format: The category of the treatment, i.e. acupuncture is listed as a “Therapy”
- Description: A short summary about the treatment benefits, risks, and administration.
Treatments are listed in alphabetical order.
Search on any term by using the search field. Sort on any column. Show more rows by increasing the display number.
| Treatment Type | Cost | Nonmedical Treatment | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive | Paid | 5-HTP (5 Hydroxytryptophan) | Vitamin/Supplement | 5-HTP is a nonessential amino acid that contributes to increased production of serotonin, melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and beta-endorphins, which all play a role in sleep, mood and pain regulation. People with migraine may have low serotonin levels. 5-HTP is directly converted to serotonin in nerve cells and the liver before it can reach the brain. Several publications have raised concern of a significant risk of heart valve disease from high levels of serotonin in the blood because of its direct effect on the heart. The supplement 5-HTP is made from a natural plant source (Griffonia simplicifolia). |
| Preventive | Paid | Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) | Behavioral therapy | Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of mindfulness-based therapy theorizing that greater well-being can be attained by accepting the difficulties that come with life, and by overcoming negative thoughts and feelings. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Acupressure | Physical therapy | Acupressure has been practiced in Asia for thousands of years. By learning how to stimulate pressure points, you may be able to relieve minor or moderate symptoms of migraine head pain and gastrointestinal distress. Acupressure can be self-administered to specific pressure points using a deep, probing pressure with fingertip, knuckle or soft, pointed object, such as a pencil eraser. If you have not found relief after the first point, try the same points on the opposite side of the body. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Acupressure bracelets | Product/Device | Bands that apply pressure on the meridian point on the inside of the wrist that is said to be associated with nausea and motion sickness. Some studies suggest there is a therapeutic benefit to magnets in alleviating pain or other health concerns. Common types include magnetic bands and Sea-Bands. |
| Preventive | Paid | Acupuncture | Procedure | A Traditional Chinese Medicine technique that involves the insertion of very fine, solid needles into certain points of the body. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, acupuncture helps headaches by encouraging the production of the body’s natural painkillers called endorphins. |
| Preventive | Free | Advocacy | Lifestyle | Advocacy is the public support of a particular cause. An example of advocacy would be supporting greater funding of migraine research, which would benefit the migraine community as a whole. |
| Preventive | Paid | Alexander Technique | Therapy | The Alexander Technique is a system designed to retrain poor posture to ensure minimum effort and strain on the body. This can help prevent headaches that result from poor posture. |
| Preventive | Free | Altruism | Lifestyle | Altruism, or the principle and practice of concerning oneself with the well-being of others, activates the reward center in the brain. Volunteering, donating to charity, or even reaching out to help a friend in need can have the added benefit of boosting your own health, happiness, and sense of purpose. |
| Preventive | Paid | Applied Kinesiology (AK) | Physical therapy | Kinesiology is the study of body movement. Applied Kinesiology (AK) is a system using basic muscle testing to evaluate areas of dysfunction within the body. AK methodology is primarily concerned with neuromuscular function and how it relates to the regulation of structural, chemical and mental physiology. It uses the principle that the body is a self-maintaining, self-correcting mechanism. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Aromatherapy | Product/Device | Aromatherapy uses plant materials and aromatic plant oils to help alter one’s mood, cognitive, psychological or physical well-being. Blends of plant oils, essential oils and other aromatic compounds are often utilized through topical application, massage inhalation, or water immersion to stimulate a desired response. Aromatherapy oils often for migraine include lavendar oil, peppermint oil, and Damascus rose oil. |
| Preventive | Paid | Ashwaghandha | Vitamin/supplement | Ashwagandha, also known as Indian ginseng or withania somnifera, is an herb used in traditional Indian medicine (i.e., Ayurveda). It is most often used to relieve stress and anxiety but may be used to treat other conditions or symptoms, such as migraine, epilepsy, joint pain, and diabetes. Ashwagandha comes in various forms, including pills, liquids, and powders. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Avoid bright screens | Lifestyle | Bright screens such as TVs, computer screens, phones, and other LED screens emit a particular spectrum of light that people with migraine may be sensitive to. Avoiding bright screens can be a way to reduce this visual trigger for those who are sensitive to bright lights. Wearing special blue-light blocking glasses can help reduce digital eye strain and fatigue when staring at computer and TV screens for prolonged periods of time. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Avoid fluorescent lighting | Lifestyle | Fluorescent lights emit a particular spectrum of light. People with migraine may be sensitive to the spectrum of light emitted by fluorescent lights. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Avoid loud, sustained noise | Lifestyle | Loud noise, constant noise, piercing, or ringing sounds are migraine triggers for some, and may worsen a person’s migraine condition for those who are vulnerable. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Avoid odors/smoke | Lifestyle | Strong odors, incense, perfume, deodorants, chemical smells, cleaning products, cigarette smoke, air pollution, vehicle exhaust, and other pungent or unnatural scents are known to be migraine triggers for some. Exposure may trigger an attack or worsen an attack in progress. |
| Preventive | Free | Avoid processed foods | Lifestyle | Processed foods often contain artificial ingredients and preservatives that can contribute to migraine. These include MSG, soy, sulfates/sulfites, nitrates, nitrites, and gluten among others. See Dietary Changes for more trigger ingredients and foods. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Ayurveda | Lifestyle | Ayurveda is an ancient Indian practice that involves a variety of treatments including yoga, massage, acupuncture, diet, and herbal medicine to encourage health and well-being. Ayurveda names three elemental substances, the doshas (called Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), and states that a balance of the doshas results in health, while imbalance results in disease. |
| Preventive | Paid | Barometer | Product/Device | Barometric pressure changes might affect the pressure in the brain or the way the brain blocks pain, though it’s not well understood at this stage. However, a barometer can help people with migraine who are sensitive to pressure changes to better anticipate this trigger and avoid other controllable triggers (e.g. food, stress) during risky weather. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Behavioral therapy apps & online tools | Product/Device | There are an increasing number of online therapy and self-care apps available to help with a variety of issues, including mental health and pain. Examples of therapy based options include Betterhelp, Talkspace and Online-Therapy.com. Mental-health and Mindfulness focused ones include Calm, Headspace, Insight Timer, Curable, iCBT, Sanvello, and MindShift. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Bio-behavioral therapy | Behavioral therapy | Bio-behavioral therapy is a pain management therapy that teaches skills for controlling physical reactions to stress and pain through relaxation and stress reduction. The idea is that stress is perhaps one of the most common behavioral factors that interacts with physical factors in the perpetuation of pain. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Biofeedback | Behavioral therapy | Biofeedback is a technique that teaches people how to control certain body functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, and spasms in the arteries supplying the brain with the help of a sensory device. Once skills are learned, they can be practiced anywhere. |
| Preventive | Paid | Black cohosh | Vitamin/Supplement | Black cohosh (Actaea racemosa) is an herb sometimes used to treat perimenopause and menopause symptoms. It is native to North America, and its roots and rhizomes are made up of glycosides (sugar compounds), isoferulic acids (anti-inflammatory substances), and phytoestrogens (plant-based estrogens). Warning: the wrong variety can lead to liver toxicity symptoms. |
| Preventive | Paid | Blood test - Food sensitivities/nutrition | Other | A food-allergy blood test may offer clues to which foods the body is reacting to, as these foods may be affecting an individual’s health and migraine. A food-allergy blood test can also determine if supplementation is necessary, by seeing if magnesium or vitamin D are deficient, for example. |
| Preventive | Paid | Blood test – Genetic dysfunction | Other | Testing for genetic dysfunctions can help uncover potential causes that may be provoking migraine attacks. For example an MTHFR and homocysteine blood test can indicate a deficiency in the processing of folate and require a specific treatment that may lead to reduced migraine. |
| Acute | Paid | Blue menthol gel | Product/Device | There are several forms of blue menthol gel on the market. It is a topical cooling gel used for pain relief, inflammation, joint swelling, etc. Blue gel can cause skin irritation. |
| Preventive | Paid | Boswellia / Indian frankincense | Vitamin/Supplement | Boswellia is an herbal extract from the Boswellia serrata tree. It is available as a resin, pill, or cream. Boswellia has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body by preventing the formation of leukotrienes. A 2012 study indicated boswellia extract can reduce the intensity and frequency of cluster headaches. |
| Preventive | Paid | Bowen therapy | Physical therapy | Bowen therapy is a holistic remedial body technique that works on the soft connective tissue of the body. It is used to treat musculoskeletal or related neurological issues, including acute sports injuries and chronic or organic conditions. Practitioners claim it is a gentle, relaxing method that does not use forceful manipulation. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Breathing relaxation techniques | Behavioral therapy | Deep breathing is a simple way to relax and reduce stress. For example, taking 3 or 10 deep, slow breaths can help reduce anxiety and control stress. Also, alternate-nostril breathing, called nadi shodhana pranayama in yoga, can help control anxiety. |
| Preventive | Paid | Butterbur | Vitamin/Supplement | Butterbur is an herbal supplement that has been reported to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks in some people with migraine. Caution should be exercised with butterbur as it contains components called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) that are toxic to the liver and may cause cancer. The concentrations of this toxin vary depending on which part of the plant is harvested and where the plant is grown. Getting butterbur from a reputable source is important. The brand name Petadolex is regarded as one of the most pure and PA-free. The long-term health effects of butterbur have not been studied. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Caffeine | Lifestyle | Caffeine is a stimulant that increases alertness, decreases fatigue, and improves muscle coordination. It is often found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and soft drinks. Caffeine is addictive. It is quickly absorbed by the body and moves rapidly to the brain. If used in excess, caffeine can be overstimulating and cause anxiety and sleep problems. Caffeine can help the body absorb some medications faster. Some sources suggest it can assist pain relievers by up to 40 percent. Caffeine is a double-edged sword for people with migraine. Any change in caffeine levels can contribute to an attack in some people. Consuming too much, too little, or skipping a day may also be a migraine trigger for some. |
| Preventive | Paid | Calcium | Vitamin/Supplement | Calcium is essential for building and maintaining bone, and is required for the healthy functioning of the heart, muscles, blood and nerves. |
| Acute | Paid | Capsaicin | Vitamin/Supplement | Hot peppers (chilis) contain a substance known as capsaicin, a natural ingredient found in many topical pain-relief creams and ointments. Capsaicin has the ability to draw something called substance-P out of your nerves. Substance-P is a chemical messenger that carries a signal to the brain that is translated as pain. When you effectively block the messenger, you block the pain, too. Use caution, as contact with skin or eyes can be dangerous. |
| Preventive | Paid | Cervical traction | Product/Device | Also known as Neck Traction. This is a method to relieve neck pain by providing an opportunity for your neck muscles and pinched nerves to be released. Tension is placed on the head to pull it up and away from the neck, stretching muscles and ligaments around the vertebrae of the spine and expanding the space between the vertebrae. Also see Occipital Lift Technique. |
| Preventive | Paid | Chinese herbal medicine | Vitamin/Supplement | Chinese herbal medicine is part of the ancient Chinese practice of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese herbal medicine takes a holistic approach to understanding the body’s normal function and disease processes, and focuses on prevention. Herbs are prescribed to restore balance to the opposing forces of energy, Yin and Yang. A Chinese herbal practitioner prescribes a specific Chinese herbal formula designed to match and treat your health problems. |
| Preventive | Paid | Chiropractor | Physical therapy | Chiropractors seek to relieve headache disorders based on the diagnosis and manipulative treatment of misalignments of the joints, particularly those of the spinal column. Manual techniques such as realignment may benefit corresponding nerves, muscles, or organs. Some medical doctors warn against allowing manipulation of the neck, which can result in a stroke. |
| Preventive | Paid | Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)/ Ubiquinol | Vitamin/Supplement | CoQ10 is a chemical naturally produced by the body and is essential for the proper functioning of cells. CoQ10 can help minimize damage to cells caused by the environment and other factors. There haven’t been many high quality trials but preliminary findings support the use of added CoQ10 for migraine treatment. A more concentrated form is known as ubiquinol. Sources of CoQ10 can be found as a supplement and naturally in most foods, with highest concentrations in the organs of animals (livers, hearts, and brains), soybeans, broccoli, dairy, avocados, the germ in grains, and most oils nuts and seeds. |
| Preventive | Paid | Cognitive Behavior Therapy (trauma focused) | Behavioral Therapy | Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy is a short-term intervention therapy for children, adolescents, adult survivors and families trying to overcome the destructive effects of early trauma such as abuse, violence, or grief. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) | Behavioral therapy | Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps people to change unhelpful or unhealthy thinking habits, feelings, and behaviors. CBT may be used to treat problems including anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, uncontrollable anger, substance abuse, eating disorders, and other problems. There is scientific evidence that supports the use of CBT for migraine. |
| Preventive | Paid | Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) | Behavioral therapy | Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is a structured program that helps people identify and replace thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems with habits that promote sound sleep. Treatment takes approximately 6-8 sessions and can be done with a therapist or via an app. |
| Acute | Paid | Cooling gel sheet | Product/Device | Applying cold items or ice packs to the head helps promote circulation and reduces the inflammation in the head caused by migraine. |
| Preventive | Free | Creative therapy | Behavioral therapy | Creative therapy includes a variety of hands-on artistic activities that slow down your mind, increase your concentration, and help you feel more present. This art-induced meditative state comes with many proven health benefits for pain relief, and less anxiety and depression. Forms include music therapy, dance/movement therapy, visual art therapy and expressive writing. |
| Preventive | Paid | Daith piercing | Procedure | The daith piercing punctures the upper lobe of the ear with an earring, and is said to correspond to an acupressure point within the ear that lines up with the digestive system. It is typically performed at a tattoo parlor. The procedure takes a long time to heal and runs the risk of infection. Experts believe it offers a temporary placebo effect for migraine relief and no lasting therapeutic value. There is currently no evidence supporting its use. |
| Acute | Free | Dark, quiet room | Lifestyle | When a migraine attack occurs, it’s been described as a malfunction where normal sensory inputs such as light, sound, or smell can cause pain. Removing yourself from these irritants can expedite your recovery, and many people find moderate to major relief in a dark, quiet room. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | Detoxification (Detox) | Lifestyle | A detox is a diet plan that requires you to follow a particular diet over a certain period of time in order to cleanse the body. It may also include (paid) herbal supplements or other methods, such as colonic irrigation, all of which aim to remove environmental and dietary toxins from the body. There is no evidence supporting its benefits or its use for migraine prevention. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - 5:2 diet | Lifestyle | The 5:2 diet is an intermittent fasting diet that has become popular after Dr Michael Mosley’s documentary on the benefits of intermittent fasting. This diet involves eating normally for five days out of a seven-day period and greatly restricting the amount of food eaten on the other two days. Preliminary studies have shown that intermittent fasting can fend off illnesses including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. It is not highly recommended for people with migraine, however, who typically respond better to a diet regime that promotes regular meals. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Anti-inflammatory diet | Lifestyle | An anti-inflammatory diet is a style of eating that centers on foods that lower inflammation in the body. Mainstays of an anti-inflammatory diet include fruits and vegetables, whole grains, beans and nuts, fish, and fresh herbs and spices. The diet is high in omega-3 fatty acids and omits foods that are processed, greasy, or sugary. Widely regarded as a healthy lifestyle choice, an anti-inflammatory diet may help in the reduction of chronic pain. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Elimination diet | Lifestyle | An elimination diet is often conducted under the guidance of a doctor or nutritionist to establish which foods are triggering migraine attacks. An elimination diet requires an individual to strip back to a few safe foods for several weeks to establish a baseline before gradually reintroducing foods one at a time, often several days apart. If a migraine attack occurs while a new food is being introduced, then it may be attributed to that food and consequently the food is removed from the diet. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet – Gluten-free diet | Lifestyle | Going gluten-free has been reported to help some people with migraine. Celiac disease occurs when the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten, leading to difficulty in digesting food. Although people with migraine do not necessarily have celiac disease, some patients may be gluten sensitive. These patients’ test results often are negative for traditional reactions to gluten, but instead show signs of a different immune reaction. If you experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and constipation, as well as fatigue and mental “fog,” it may be worth trying a gluten-free diet. There is, however, no strong evidence linking this diet to migraine. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - High in omega-3/low in omega-6 | Lifestyle | Eating a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids can decrease the frequency of headaches in persons with migraine. Eating a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in omega-6 fatty acids can further decrease headache frequency in persons with migraine. Foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids include deep cold-water fishes (e.g., mackerel, salmon, sardines), krill, and flax seeds. Intake of omega-6 fatty acids can be reduced by avoiding processed foods and adding in more fruits and vegetables. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Ketogenic diet | Lifestyle | This is a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate, low-sugar diet that in medicine is used primarily to treat difficult-to-control epilepsy in children. In small case studies, migraine has been shown to improve while on a ketogenic diet. Further study is needed. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Mediterranean diet | Lifestyle | The Mediterranean diet is modeled after the traditional diets of Mediterranean countries like Italy and Greece. The diet is considered anti-inflammatory and is often recommended as a means of preventing disease and promoting longevity. Main components include a high intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats (such as olive oil); frequent consumption of fish, poultry, nuts, and eggs; and limited consumption of dairy and red meat. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Paleo diet | Lifestyle | The Paleo diet, also known as the Caveman or Stone Age diet, mimics the hunter-gatherer diet of our Paleolithic ancestors. It promotes consumption habits that avoids grains, legumes, and some dairy products in favor of the foods available to our ancestors during this period. Caution should be taken, as any diet that excludes entire food groups may be detrimental. Published studies for the diet are small, with too few participants to claim reputable scientific evidence. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Vegan diet | Lifestyle | Vegans, in addition to being vegetarian, do not use other animal products and by-products such as eggs, dairy products, honey, leather, fur, silk, wool, cosmetics, and soaps derived from animal products. There is no evidence linked to migraine improvement. |
| Preventive | Free | Diet - Vegetarian diet | Lifestyle | Vegetarians do not eat meat, fish, or poultry. There is no evidence linked to migraine improvement. |
| Preventive | Free | Dietary changes | Lifestyle | What you eat can play a significant role in your migraine. There are a number of foods that are problematic for a large number of migraine sufferers. Understanding which foods, if any, trigger your migraine attacks can be essential to successful migraine management. Common food triggers to be aware of are food additives such as nitrites and MSG (monosodium glutamate), food coloring, chocolate, aged cheese, red wine, beer, caffeine, citrus fruits, cured meats, aspartame and ice cream. If you are unsure, it may be worthwhile speaking with your doctor or seeing a dietitian or nutritionist to manage your diet. They can also help determine if you have any food allergies that may be contributing to your migraine attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | D-Ribose (Beta-D-ribofuranose) | Vitamin/Supplement | D-Ribose is a type of sugar that is produced by the body which can be used as a supplement. It’s often used to improve athletic performance and the ability to exercise by boosting muscle energy. It has also been used to help prevent cramping, pain, and stiffness after exercise in those with genetic disorders. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Dry needling | Physical therapy | Dry needling is a treatment performed by trained physiotherapists (or physical therapists) that involves inserting thin, filament needles into trigger points — knotted parts of the muscle that affect function and motion and can cause pain. Dry needling can help alleviate tension and allow muscles to return to a relaxed state. In a person with migraine, dry needling could especially help improve pain in the muscles of the temples, jaw, neck, shoulders, and back of the head. For those for whom muscle tightness is a trigger, dry needling could serve as a preventive treatment for migraine. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminate cigarette smoking | Lifestyle | Quitting smoking is a smart choice for your health. Cigarette smoke contains over 4,000 chemicals including 43 known cancer-causing (carcinogenic) compounds and 400 other toxins. Apart from the obvious health benefits, cigarette smoke is a trigger for some people with migraine, and the chemical damage to an individual’s health that results from smoking is likely to make existing health conditions worse. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating alcohol | Lifestyle | Alcohol causes headaches even for people who don’t experience migraine. If you are susceptible to migraine and you drink alcohol, it is almost always a contributing factor. It is one of the least disputed food triggers for migraine because it is so common. About a third of migraine sufferers list alcohol as a trigger. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating caffeine | Lifestyle | While caffeine has its advantages (see Caffeine for detail), for many people with migraine, the disadvantages outweigh the benefits. Consequently, a person with migraine may gradually wean down and eventually eliminate their caffeine consumption over time. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating chocolate | Lifestyle | Some people with migraine list chocolate as a trigger food. Some neurologists say it is a migraine trigger because it contains the amino acid tyramine. The connection could also be that some people tend to crave chocolate during stress and hormonal changes, both of which may also trigger headaches. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating dairy | Lifestyle | Dairy can be a migraine trigger for some. Much of the world's population is lactose intolerant and can't consume large amounts of dairy foods. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating gluten | Lifestyle | See ‘Diet – Gluten-Free’ |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating MSG | Lifestyle | MSG, or monosodium glutamate, is an amino acid used as a food preservative and flavor enhancer. It has been named as a common migraine trigger. It is not limited to Chinese food and has many aliases, making it difficult to detect on packaged foods ingredient listings. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating nitrates/nitrites | Lifestyle | Nitrates are converted into nitrites once they are digested. Foods high in artificially added nitrates have been linked to migraine as well as a potentially higher risk of cancer. Processed meats such as bacon, hot dogs, sausages, cured ham, cold cuts, and related products commonly have artificially added nitrates as a preservative. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating soy | Lifestyle | Soy has been linked to migraine in some people. In addition to soy beans, soy products are often included in breads, crackers, cakes, rolls, processed cereals, canned soups, ice cream, frozen desserts, margarines, butters, salad dressings, sauces, breakfast bars, and other products, as well as soy sauce, soy lattes, tofu, and miso. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating sulfates/sulfites | Lifestyle | Sulfates are found commonly in wine as a preservative, though some preservative-free wines are now available. Sulfates are thought to be a reason why wine is a significant migraine trigger. Sulfate is also used as a preservative in dried fruit and many dried-fruit products. |
| Preventive | Free | Eliminating tyramine | Lifestyle | Tyramine has been recognized as a common migraine trigger, though experts are still trying to understand why. One explanation might be that tyramine can cause nerve cells in the brain to release a chemical called norepinephrine, and the norepinephrine may cause changes in the brain that lead to migraine. Tyramine is found in red or balsamic vinegar, aged cheeses, chocolate, smoked fish, bacon, sausages, hot dogs, avocado, red plums, bananas, citrus fruits, olives, processed meats, and some types of alcohol. |
| Acute | Free | Emotional freedom technique (EFT) | Behavioral therapy | Emotional freedom technique (EFT), also referred to as "tapping", is an alternative treatment for physical pain and emotional distress. EFT involves fingertap tapping on the meridian points (like the ones used in acupuncture) to restore the body's energy, which can lead to relieving symptoms of a negative experience or emotion. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Epsom salt baths | Product/Device | Magnesium sulfate is the scientific name for Epsom salt. The magnesium and sulfates in Epsom salt are apparently absorbed through the skin and may increase the magnesium levels in your body. Epsom salt baths are popular for softening and exfoliating skin, relaxation, drawing impurities out of skin and relieving migraine and cold or flu symptoms. Consult with your physician before taking Epsom salt baths if you are pregnant or have a medical condition. |
| Preventive | Paid | Essential oils | Product/device | See Aromatherapy. |
| Acute | Paid | Evening primrose oil | Vitamin/Supplement | Evening primrose oil contains “fatty acids” which are thought to help decrease inflammation related to conditions like arthritis or migraine. Evening primrose oil has been used for a range of disorders, including skin complaints such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne. It is also used for other conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, high cholesterol, and heart disease. |
| Preventive | Free | Exercise | Lifestyle | Exercise helps with rest and relaxation and it also helps release stress, a common trigger for migraine. Most experts recommend at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily to get the best results for stress reduction. If you can find things you enjoy doing, you’re more likely to be consistent. Anything is better than nothing. If exercise triggers migraine, however, start small. If you’re outside, wear polarized sunglasses. Ensure that you’ve eaten enough and stay hydrated. Starting small and building upwards is a much more successful approach than trying to jump in without preparation. Many people with migraine find yoga, Pilates, or t’ai chi to be great low-impact options. |
| Preventive | Paid | Feverfew | Vitamin/Supplement | Feverfew is an herb with leaves containing natural anti-inflammatory qualities. It may prevent the release of blood-vessel dilating substances in the brain and may reduce inflammatory substances from developing, both of which can increase pain levels. It does provide relief for some sufferers and, given its low side effects, it is a relatively low-risk option. |
| Preventive | Paid | Folate | Vitamin/Supplement | Folate is also known as folic acid or vitamin B9. This vitamin is important for cell growth and metabolism. Folate is the natural version found in foods, and folic acid is the man-made version found in supplements and added to foods. See Folic Acid for more details. |
| Preventive | Paid | Folic acid / Vitamin B9 | Vitamin/Supplement | Folic acid is a type of B vitamin that is normally found in foods such as dried beans, peas, lentils, oranges, whole-wheat products, liver, asparagus, beets, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and spinach. Folic acid helps your body produce and maintain new cells, and also helps prevent changes to DNA that may lead to cancer. As a medication, folic acid is used to treat folic acid deficiency and certain types of anemia (lack of red blood cells) caused by folic acid deficiency. |
| Preventive | Free | Forest bathing | Lifestyle | Forest bathing is a Japanese technique that involves sitting in the forest and being surrounded by greenery. In Traditional Chinese Medicine this is one of the treatments for issues relating to the Wood element, which includes migraine. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Ginger | Vitamin/Supplement | Ginger is an herb known for its antinausea, antidiarrhea, and digestion-aiding properties. It can be consumed in many forms including raw, as powders, in supplements and in ginger ale. Ginger is used in migraine to alleviate the symptoms of nausea and vomiting. Ginger root can also be used in the treatment of migraine. Ginger contains more than 200 substances in its oils that help facilitate its many roles. For migraine, it is thought that ginger may block prostaglandins, which stimulate muscle contractions and control inflammation and some hormones. |
| Preventive | Paid | Glucosamine | Vitamin/Supplement | Glucosamine is a natural chemical compound found in the body. As a supplement, glucosamine is most often used to try to ease the joint pain caused by arthritis. |
| Acute | Paid | Green-Light Lamp, The Allay Lamp | Product/Device | Therapeutic light device designed to reduce anxiety and migraine intensity during an attack. It is based on scientific evidence from seven years of research at Harvard Medical School. The studies show that light made up of all the colors of light (red, blue, yellow, etc.) generates large electrical signals in the eye and brain, which tend to hurt people with light sensitivity. A very specific narrow band - which is the only light emitted by the Allay Lamp - generates smaller electrical signals in the eye and brain. |
| Acute | Free | Heat therapy | Lifestyle | Heat therapy can increase blood flow to muscles and help relax them. Heat therapy can also stimulate nerve endings, which may block pain signals from the affected area to the brain. Examples of heat therapy include heating pads, heat lamps, hot packs, and hot water bottles. If the temperature of the heat therapy becomes too high, discomfort or even burns may occur. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Herbal teas | Vitamin/Supplement | Herbal teas contain vitamins and nutrients. Drinking hot herbal tea can also be a calming and relaxing activity that helps with hydration. Commonly used teas to help with migraine related symptoms include Dandelion, Chamomile, Ginger, and Mint. |
| Preventive | Paid | Homeopathy | Therapy | Homeopathy is a form of alternative medicine that claims to stimulate the body’s own healing response to disease using highly diluted preparations (potentizing). There are no effective homeopathic vaccines, and homeopathic treatments should not be used to replace conventional medical treatment of serious diseases or infections. The effectiveness of homeopathy has not been proven by medical science. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Hydration | Lifestyle | Dehydration is a common migraine trigger. Keeping water on hand throughout the day helps ensure you get the recommended eight glasses per day. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Hydrotherapy | Lifestyle | Hydrotherapy involves the use of water for pain relief and treatment. Using ice packs on the head or splashing the face with cold water can help provide relief. Having hot and cold showers dilates then constricts blood vessels, which stimulates circulation. Exercise in water, such as water aerobics, is another form of hydrotherapy. |
| Preventive | Paid | Hyperbaric oxygen therapy | Therapy | Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is an immersive, enclosed chamber where 100 percent oxygen flows with no mask or cannulae. It does not require a prescription. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy hasn’t been shown to be as effective for migraine as it is for cluster headache. See Oxygen in Medical Treatments. |
| Preventive | Paid | Hypnotherapy/ Hypnosis | Therapy | Hypnosis is the induction of a state of consciousness in which a person apparently is highly responsive to suggestion or direction. Its use in therapy to recover suppressed memories or to allow modification of behavior is controversial. |
| Acute | Free | Ice/cold therapy | Product/Device | Cold slows down blood flow to an injury, thereby reducing pain and swelling. Cold therapy slows circulation, reduces inflammation, muscle spasms, and pain. It is often found to be helpful for people wanting to "take the edge off” a migraine attack by applying ice or cooling gel sheets to painful areas on the head. Wearable ice packs permit sleeping and movement while worn. |
| Preventive | Free | Improving posture | Lifestyle | Poor posture can result in tightening muscles in the neck or scalp, which may lead to headache and migraine. Extended reading looking down at a mobile phone or hunching over a computer, laptop, or gaming console can lead to neck and back pain and can trigger an attack. Modern laptops encourage poor posture. Correcting postural issues may help relieve migraine and reduce the frequency of attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | Iron supplements | Vitamin/Supplement | Iron is a mineral found naturally in foods as well as a vitamin supplement. Iron is required for growth, development, normal cellular functioning, and synthesis of some hormones and connective tissue. |
| Preventive | Paid | Isoflavones | Vitamin/Supplement | Isoflavones (e.g. Promensil) are polyphenolic compounds that are capable of exerting estrogen-like effects. For this reason, they are classified as phytoestrogens – plant-derived compounds with estrogenic activity. Legumes, particularly soybeans, are the richest sources of isoflavones in the human diet. |
| Preventive | Paid | Krill oil | Vitamin/Supplement | Krill oil capsules are a more highly concentrated form of omega-3 fats than fish oil capsules, with similar benefits. The omega-3 fats EPA and DHA play an important role in emotional health, and deficiencies have been linked to mood disorders. Krill oil helps reduce inflammation, which causes pain. (See Omega-3). |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Lavender oil | Vitamin/Supplement | Lavender oil may help reduce nervous tension and pain, and enhance blood circulation. Its calming scent makes it a popular choice for anxiety issues. It is also used as a natural alternative to help with insomnia. |
| Preventive | Paid | L-carnitine | Vitamin/Supplement | L-carnitine is an amino acid naturally produced by the body. It can be used as a supplement when natural levels are low or for those on a vegetarian diet. Not FDA approved for migraine. |
| Preventive | Paid | L-methylfolate / Levomefolic acid | Vitamin/Supplement | L-methylfolate is a particular type of folic acid supplement that provides the body with folate. It can assist in the management of low plasma or low red blood cell folate in patients. |
| Preventive | Paid | Magnesium (including variants i.e., citrate, glycinate, threonate oxide) | Vitamin/Supplement | During a migraine attack, low levels of magnesium have been shown in the brain. It’s thought that magnesium deficiency and migraine may be related since magnesium is required for proper nerve function. Magnesium as a preventive may be especially helpful for those with hormonal migraine. Sources of magnesium include legumes, nuts, whole grains, seeds, leafy green vegetables, soy products, bananas, dried apricots, avocados, and supplements. Dr. Mark Hyman recommends a high dose of magnesium citrate or glycinate at 300-600 mg twice per day to help prevent migraine attacks. Magnesium threonate may be used to improve sleep if one has trouble falling asleep. |
| Preventive | Paid | Magnotherapy | Therapy | Also known as magnet therapy or magnetic therapy. It is an alternative practice involving the use of static magnetic fields. Practitioners of magnotherapy claim that subjecting certain parts of the body to magnetostatic fields produced by permanent magnets has beneficial health effects. These physical and biological claims are unproven and no effects on health or healing have been established. |
| Preventive | Free | Manage stress | Lifestyle | Stress in its many forms is one of the most significant factors for people with migraine. Stress can come from strong emotions, both negative and positive. But it can also descend into anxiety, panic attacks, and depression. Stress can easily creep up on you. You get used to it. It can feel familiar or even normal without any realization of the heavy toll it takes. Stress can be beneficial at a mild level, but beyond a certain point it starts causing major damage to your health, particularly in relation to migraine conditions. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Meditation | Behavioral therapy | Recent research has shown very promising results for meditation, with all participants reporting less severe migraines as well as other benefits including reduced stress, less anxiety, better sleep, better general health, concentration, self awareness, and self control. |
| Preventive | Paid | Melatonin | Vitamin/Supplement | Melatonin acts on the receptors for many pain-relieving molecules in the brain (e.g. opioid receptors), leading to a decrease in pain sensations when melatonin levels are high. Melatonin supplements have been shown to lower pain intensity, and a clinical trial found that 3 mg of melatonin 30 minutes before bedtime helped to reduce the overall frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine headaches for the subjects in the study. |
| Acute | Paid | Menthol/Mint, Camphor | Vitamin/Supplement | Peppermint and menthol are numbing and calming, making them useful to soothe the overactive nervous system during a migraine attack. It can be inhaled, applied topically, or ingested. There’s growing evidence that menthol for migraine is just as effective as over-the-counter medications to treat an attack in the early stages. Camphor is a waxy terpene commonly used in creams ointments, and lotions. It has a wide variety of topical uses, including as an anti-inflammatory. Can be used to treat mild to moderate pain. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | Migraine Buddy | Product/Device | Using a migraine app means being able to go to your doctor with proper documentation to answer questions such as, "How many migraine days do you have? How many types of treatments are you taking?" It also assists with identifying potential triggers, showing how migraine evolved with the treatment provided and the level of relief with those treatments. |
| Preventive | Paid | Migraine Support Formula | Vitamin/Supplement | This is a multivitamin product designed specifically for people with migraine, which combines several well-known vitamins and supplements to help relieve migraine into one pill. Vitamins included are riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, magnesium, ginger, CoQ10, white willow, feverfew, butterbur & black pepper. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Mindfulness | Lifestyle | A form of meditation based on a moment-by-moment awareness of thoughts, feelings, bodily sensations, and surrounding environment. It means tuning in to the present moment, paying attention to thoughts and feelings without judgment. Though it has its roots in Buddhist meditation, mindfulness has entered the mainstream in part through the work of Jon Kabat-Zinn and his Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program. Thousands of studies have documented the mental and physical benefits of MBSR, often used in pain reduction. |
| Preventive | Paid | Myofascial release | Physical therapy | Myofascial release (MFR) is a soft-tissue therapy for the treatment of skeletal muscle immobility and pain. This alternative medicine therapy aims to relax contracted muscles, improve blood and lymphatic circulation, and stimulate the stretch reflex in muscles. |
| Preventive | Paid | N1-Headache app | Product/Device | N1-Headache is a smartphone app that allows users to track migraine symptoms, triggers, and medications for 90 days and then produces an individualized report. N1 can identify triggers and protectors and is able to eliminate nonrelevant factors. This approach can help untangle the interactions between triggers and protectors that govern attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | Naturopathy | Therapy | Naturopathy is a holistic approach to wellness based on the principle that the body has the inherent ability to heal itself. Using gentle therapeutic techniques, the body, mind, and emotions are supported during the healing process. Naturopathic medicine has been criticized for its lack of scientific evidence and conflicts with evidence-based medicine. For example, many naturopaths oppose vaccination. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Neck/Scalp massage | Physical therapy | Massage involves working and acting on the body with pressure that is either manual or with mechanical aid. Peer-reviewed medical research has shown that massage can help with pain relief, anxiety, and depression, as well as temporarily reduce blood pressure and heart rate. |
| Preventive | Paid | Niacin / Vitamin B3 | Vitamin/Supplement | Vitamin B3 helps release energy from carbohydrates, fats, and cholesterol while regulating blood sugar levels. Supplemental vitamin B3 causes the face and skin to flush, which is thought to help release the pressure of a migraine headache. |
| Preventive | Paid | Night or Mouth guard | Product/Device | A dental guard (occlusal splint, mouth guard, night guard, or bite plate) is a custom-fitted dental device meant to prevent teeth grinding and jaw clenching, either while awake or asleep. Mouth guards not only protect the teeth but can also alleviate jaw and head pain that occurs from bruxism, or clenching and grinding of the teeth. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Noise-cancelling headphones | Product/Device | Noise-canceling headphones block out ambient sound and background noise. Reduction in noise can be helpful for those with sound sensitivity during a migraine attack and in preventing migraine if noise is a trigger. Noise-canceling headphones are widely available by most major brands including Bose, Sony, Apple, Beats, Bang & Olufsen, and JBL, etc. |
| Preventive | Paid | Nutraceuticals | Vitamin/supplement | Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that provide nutrition and medicinal benefits. Examples of nutraceuticals include dietary supplements, diets, herbal products, and vitamins. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Occipital lift technique | Physical therapy | Typically performed by a manual therapist, for example a physiotherapist or chiropractor, the occipital lift technique is where the therapist gently lifts the head away from the neck to allow for a release in tension and muscle relaxation. Practitioners believe that this practice may facilitate an increase in venous and lymphatic drainage from the skull, improve circulation, promote relaxation, and reduce blood pressure, all of which can relieve headaches. |
| Preventive | Paid | Omega-3 | Vitamin/Supplement | Omega-3 fatty acids are found mostly in fish and fish oils but also in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. According to the American Heart Association, the omega-3 in fish oil may reduce inflammation, aid in preventing blood clotting, improve blood pressure, and steady the heart rhythm. This may be useful in the reduction of migraine as it may reduce inflammation in the head. Sources of fish oil can be obtained from taking supplements or by eating fish including mackerel, tuna and salmon, among others. |
| Preventive | Paid | Osteopathy | Physical therapy | Osteopathy is a type of alternative medicine physical therapy that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bone. It can be used to correct misalignments that may trigger migraine attacks in some people. |
| Acute | Free | Passage of time | Lifestyle | While not technically considered a treatment, the passage of time is one of the most common tactics people with migraine employ to get over the worst part of their attacks. Resorting to “waiting it out” may be due to a lack of effective acute treatment, lack of knowledge about available treatments, or a lack of willingness to try new options with the help of a doctor. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Pedialyte | Vitamin/Supplement | Pedialyte is designed to promote rehydration and electrolyte replacement in ill children. Compared to Gatorade, Pedialyte contains more sodium and potassium, and does not contain sucrose, but may contain synthetic sweeteners. |
| Preventive | Paid | Peppermint oil | Vitamin/Supplement | Peppermint oil is used for a variety of health conditions and can be taken orally in dietary supplements or topically as a skin cream or ointment. Some evidence suggests that peppermint oil may help relieve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and indigestion. Despite promising findings, there is no clear-cut evidence to support its use for other health conditions. Its use is not advisable for pregnant women. |
| Preventive | Free | PERMA™ Theory of Well-Being | Behavioral therapy | PERMA™ Theory of Well-Being focuses on five building blocks that enable an individual's flourishing: Positive Emotion, Engagement, Relationship, Meaning, and Accomplishment. There are techniques to increase each building block and the process will vary from person to person. Having a greater sense of well-being can help with having fewer sleep problems, lower levels of burnout, and better self-control and coping abilities. |
| Preventive | Paid | Petadolex (butterbur extract) | Vitamin/Supplement | Butterbur is an herbal supplement that has been reported to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine in some people with migraine. However, caution should be exercised with butterbur, as it contains components called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), which are toxic to the liver and may cause cancer. The concentrations of this toxin vary depending on which part of the plant is harvested and where the plant is grown. Petadolex is a brand name of the vitamin producer whose makers claim that it doesn’t contain the harmful chemicals (PAs) within butterbur. |
| Preventive | Paid | Physiotherapy / Physical Therapy | Physical therapy | Physical therapy or physiotherapy has the potential to release pressure, tension, strain, or injury that may lead to headaches. It is also a medically respected approach to treat physical ailments. People with migraine are known to have a number of trigger points in the shoulders, back, and neck. Releasing these areas may be particularly useful to help desensitize nerves, which may be leading to migraine, particularly if you feel your migraine attacks are caused by neck issues. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | Pilates | Lifestyle | Pilates is a system of exercise with or without special apparatus, designed to improve physical strength, flexibility, and posture, and enhance mental awareness. The two primary types are Mat Pilates, which can be done for free or in a paid class; and Reformer Pilates, which requires the use of a specially designed table and is usually done with a paid instructor at a studio or physical therapy office. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Pillow (Shaped or Cooling) | Lifestyle | A pillow that supports the natural curve of the neck can help to reduce neck pain and improve sleep quality. A pillow with a cooling segment can be comforting during a migraine attack. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Placebo response | - | Occurs when a person perceives an improvement (a nocebo response is a negative response or worsening) in symptoms or overall health after receiving a treatment or medication. This is from the psychological effect of receiving this treatment/medication, rather than the treatment/medication itself. Sometimes a sugar pill is enough to improve a person’s condition because of this effect. This is a powerful effect and could be even more so if harnessed into a treatment. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Prayer | Lifestyle | Prayer can provide comfort, strength, and reassurance for those who practice it as part of their faith. It offers hope for those who are dealing with chronic pain and health issues. |
| Preventive | Paid | Probiotics | Vitamin/Supplement | Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your digestive system. Increasing evidence considers the gut to be the “second brain,” and the gut-brain connection to be a significant factor in our well-being. They can be consumed through supplments or naturally in many fermented foods including certain yogurts, pickles, sauerkraut, miso, tempeh, kombucha, sourdough bread, and some cheeses. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Progressive muscle relaxation therapy | Behavioral therapy | Progressive muscle relaxation, also known as Jacobson's relaxation technique, involves tensing a group of muscles while breathing in, then relaxing them while breathing out. Muscle groups are tensed and relaxed in sequence until the entire body is relaxed. This strategy is helpful for migraine, anxiety, and general stress management. |
| Acute | Paid | Psilocybin | Vitamin/Supplement | Psilocybin is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by various species of mushrooms. The prodrug is converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar to LSD and mescaline. Psilocybin has been reported to abort cluster headache attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | Psychotherapy | Behavioral therapy | Psychotherapy is a general term for treating mental health problems or emotional difficulties by talking with a psychiatrist, psychologist, or other mental health provider. Psychotherapy can help a person to take control of their life and respond to challenging situations with healthy coping skills. For persons with chronic conditions, psychotherapy can help with accepting the diagnosis and condition, making adjustments to everyday life, and managing related emotions and stresses. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Qigong | Lifestyle | Qigong practice involves posture or movements, breathing techniques, and mental focus, which aim to integrate and cleanse the body and mind. Qigong is a type of mind-body training; regular practice helps physical relaxation and mental calm. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | Reflexology | Physical therapy | Reflexology is an alternative medicine involving the application of pressure to the feet and hands with specific thumb, finger, and hand techniques without the use of oil or lotion. It is based on a system of zones and reflex areas that purportedly reflect an image of the body on the feet and hands, with the premise that such work affects a physical change to the body. |
| Preventive | Paid | Reiki | Physical therapy | Reiki is a technique commonly called palm healing or hands-on healing. Through the use of this technique, practitioners believe that they are transferring "universal energy" through the palms of the practitioner, which they believe encourages healing. It is based on “qi,” which practitioners say is a universal life force, although there is no empirical evidence that this life force exists. Global cancer societies state that Reiki should not be a replacement for conventional treatment of diseases such as cancer, but that it may be used a supplement to standard medical treatment. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free & Paid | Relaxation techniques | Behavioral therapy | Relaxation techniques help control stress. They can also help you fall asleep faster. Common relaxation techniques include meditation, t’ai chi, massage, and deep breathing. |
| Preventive | Paid | Remedial massage | Physical therapy | Remedial massage, also known as medical masssage or sports massage, is a type of massage that focuses on relieving muscle tension and treating chronic pain. It can can reduce headaches by relieving muscle tension throughout the body. |
| Preventive | Free | Resilience | Lifestyle | Resilience is the process of adapting well (or "bouncing back") in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats, or significant sources of stress. Resilience helps people get through difficult circumstances and also empowers them to grow and improve their life along the way. |
| Acute | Free | Rub/pressure temples | Lifestyle | Rubbing or placing pressure on the temples can be a self-massage technique that is sometimes known as "the temple rub.” It’s simple to apply. Take deep breaths and rub your temples in gentle circles. Rubbing your temples in forward circles toward your ears and nose is generally the direction suggested. Do so for at least 10 circles and 10 deep breaths. It is claimed to help relieve headache and neck aches. |
| Preventive | Paid | Saffron | Vitamin/Supplement | Saffron contains several plant-derived chemical compounds that are known to be antioxidant, disease preventing, and health promoting. It is also an excellent source of vitamins and minerals including vitamin A, folic acid, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, copper, potassium, calcium, manganese, iron, selenium, zinc, and magnesium. |
| Acute | Paid | Salt Crystals/Salt lamps | Vitamin/Supplement | Natural salts such as Himalayan salt contain numerous minerals and electrolytes. Taking 2 teaspoons mixed with lemon juice in a cup of water may help a migraine attack. Salt lamps — which are thought to help purify the air by attracting moisture, humidity, and other airborne water molecules — may also be used. |
| Preventive | Free | SEEDS | Lifestyle | SEEDS is an acronym for a lifestyle management technique. It stands for regular Sleep, regular Eating, regular Exercise, Drinking water (staying well-hydrated and avoiding caffeine and alcohol), and Stress reduction. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Self-acupressure | Physical therapy | Acupressure is an ancient practice of using the fingers to gradually press key healing points, which stimulate the body's natural self-curative abilities. Self-acupressure is the practice of pressing on these certain points yourself, rather than by an acupressure practitioner. There are many different points, but the Hoku Point (LI4), just behind the webbing between your thumb and index finger, is considered helpful in relieving headaches. |
| Preventive | Paid | Shiatsu | Physical therapy | Shiatsu is a Japanese form of massage therapy that involves targeted hand pressure to certain body points to help restore the “energy balance” and promote relaxation. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Sleep | Lifestyle | Sleep is a restorative brain function that affects many other aspects of bodily function. It is a vital and often neglected area for people with migraine. Sleep helps the body to heal itself. It powers down areas of the body so that recovery and repair can be performed. As a preventive measure, good sleep hygiene is a practice that ensures at least 7-8 hours per night on a consistent sleep/wake cycle. As an acute treatment, many people list sleep as one of the most effective acute treatments for migraine. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Sleeping mask | Product/Device | A sleeping mask is a simple tool used to cover the eyes to facilitate sleep in an area with distracting lights. If you are woken by light early in the morning, wearing a sleeping mask may facilitate more sleep after the sun has risen. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Smartphone and computer-screen filters | Product/Device | Smartphone filters, such as Apple's Dark Mode, in which users can choose a dark palette for all screens, views, menus and controls. Contrast and transparency can be adjusted for comfort and legibility. For computer screens, f.lux is a free software that changes a user's computer dispay to adapt to the time of day: warm at night, and like sunlight during the day. Such filters are said to promote better sleep. |
| Preventive | Free | Smell retraining therapy | Physical | Smell retraining therapy is typically used as a treatment for loss of smell. It helps to rebuild the connection between the nose and the brain to recover the sense of smell. It involves sniffing several potent scents for 10-15 seconds each time, 2-4 times/day, for 10-16 weeks. The most recommended scents are rose, lemon, cloves, and eucalyptus. |
| Preventive | Free | Social connection | Lifestyle | Social connection is the feeling of belonging to a group and feeling close to other people. The support one receives from their social connections can add to the feelings of meaning and purpose in life, which then contributes to resilience. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Social support | Lifestyle | Social support can be broken down into four forms. Emotional: people who offer the proverbial shoulder to cry on. Informational: people you can go to for advice and information. Belonging: people who give you the sense that you're not alone, you're part of a family or a community. Esteem: people who make you feel like you have value and worth. |
| Acute | Paid | Sports Drinks | Product/Device | Sport drinks like Gatorade and Powerade that aid in rehydration contain a mixture of helpful electrolytes including sodium and potassium, as well as sugar and water. Electrolytes are required for hydration and proper nerve and muscle function. |
| Preventive | Paid | St. John’s Wort | Vitamin/Supplement | St. John’s Wort is most used for depression and conditions that sometimes go along with depression, such as anxiety, tiredness, loss of appetite, and trouble sleeping. There is scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness for mild to moderate depression. The evidence for migraine is inconclusive. Consult your Doctor before taking it as many contraindications exist for St. John's Wort. |
| Preventive | Free | Stretching | Lifestyle | Stretching can be beneficial in relieving muscle tension that can lead to stiffness and pain. Neck exercises and shoulder shrugs can be helpful in keeping the area around the neck and head limber. It also helps settle trigger points. Next time you feel an oncoming attack, try a few gentle stretches and see if it helps alleviate the attack. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | T’ai Chi | Lifestyle | T’ai chi is a form of traditional Chinese exercise that purports to improve health by changes in mental focus, breathing, coordination, and relaxation. The goal of t’ai chi is to “rebalance” the body's own healing capacity. It has been practiced in China for hundreds of years. A 15-week intervention of t’ai chi practice was effective in reducing headache impact and also effective in improving perceptions of some aspects of physical and mental health. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | THC | Vitamin/supplement | THC is a psychoactive compound of marijuana used by some for preventive or acute migraine treatment. THC and marijuana are controlled substances in the U.S., prohibited by federal law. |
| Preventive | Paid | Tinted migraine glasses and contacts | Product/Device | Migraine glasses or contacts fitted with an FL-41 tint, offered in indoor and outdoor tints, reduce glare and blue light from digital screens. People with photophobia and light sensitivity as a trigger may find benefit with these products. Yellow-tinted and amber-tinted lenses are popular choices for managing light sensitivity. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Trigger point injections | Physical therapy | Trigger points are knotted or tightly banded areas of a muscle; when pressed, it can produce pain within the muscle and even pain in other areas (called "referred pain"). Trigger points within the muscles of the head, neck, and shoulders can cause migraine attacks by themselves — or they can be a result of migraine attacks. Trigger point injections involve the inserting of numbing medication into the trigger point to relieve pain in the affected areas. They are typically performed by doctors in an outpatient setting. |
| Preventive | Paid | Triphala | Vitamin/Supplement | Triphala means “three fruits.” Triphala is a traditional Ayurvedic herbal formulation consisting of Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Bibhitaki (Terminalia belerica), and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula). Triphala is most commonly known for its use as a gentle bowel tonic, being helpful in digestion, and assisting natural internal cleansing. |
| Preventive | Paid | Turmeric | Vitamin/Supplement | Turmeric is an herb that contains curcumin, a substance with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. |
| Preventive | Paid | Valerian | Vitamin/Supplement | Valerian is an herb. The roots are used as a muscle relaxer. Outside of migraine treatment, valerian is most commonly used as a sleep aid. It can also be helpful for stress and anxiety. You can find valerian as a supplement as it is not easily found in food. |
| Acute & Preventive | Paid | Vapor inhaler stick | Product/Device | Often using menthol as the active ingredient, inhaler sticks may be used to treat nasal congestion and help clear the sinuses, which may be adding pressure or contributing to a migraine attack. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vestibular rehabilitation | Physical therapy | For people who experience severe dizziness or vertigo with migraine, vestibular rehabilitation offers an exercise-based program to help restore vestibular function and balance. Depending on the problems identified, three principal methods of exercise can be prescribed: 1) Habituation, 2) Gaze Stabilization, and/or 3) Balance Training. |
| Preventive | Paid | Visceral manipulation | Physical therapy | Visceral manipulation is a gentle manual technique involving specific placement of soft manual forces to encourage the normal mobility, tone, and motion of the viscera (internal organs) and the connective tissue and ligaments that support each organ onto our skeleton. Specific techniques are used to evaluate how abnormal forces might be affecting your normal body functions or affecting your skeleton, soft tissues, and organs. Techniques are then used to gently assist releasing the tension lines and improve visceral mobility. These manipulations are believed to improve the functioning of individual organs, the systems the organs function within, and the structural integrity of the entire body. There is not conclusive evidence to support visceral manipulation. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vision Therapy / Eye Exercises | Physical therapy | Eye exercises are thought to help improve vision and strengthen the muscles surrounding the eye that assist with normal function. Scientific evidence for eye exercise regimes are controversial with little evidence to support some of the claims made by practitioners. It is thought that with better vision comes less visual strain, which may contribute to migraine attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitamin B complex | Vitamin/Supplement | This is a multivitamin that includes a range of B vitamins. Some of the benefits from a B-complex multivitamin may include energy production, a healthy function of the nervous system and assisting in the conversion of food to energy. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitamin B12/Cobalamin | Vitamin/Supplement | The key role of vitamin B12 is the normal functioning of the brain, the nervous system, and the formation of blood. It is involved in the metabolism of every cell of the human body. Vitamin B12 is found in most animal-derived foods including fish, shellfish, meat (especially liver), poultry, eggs and milk. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitamin B2/Riboflavin | Vitamin/Supplement | Riboflavin/vitamin B2 has been reported as useful in migraine treatment due to its role in helping heal and strengthen brain cells. This can be taken as a supplement or by consuming foods high in vitamin B such as milk, cheese, leafy vegetables, liver, kidneys, legumes, yeast, mushrooms, almonds, soybeans, wheat bran, salmon, and sun-dried tomatoes. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitamin B6/Pyridoxine | Vitamin/Supplement | Vitamin B6 is involved in the process of making serotonin and norepinephrine, which are chemicals that send signals to the brain. Vitamin B6 is also involved in the formation of a protein layer around the nerve cells called myelin. Deficiencies in this vitamin may cause health issues affecting the nerves, skin, and circulatory system. Mild deficiency of vitamin B6 is common. Sources of B6 include cereal, grains, legumes, vegetables (carrots, spinach, peas, potatoes), milk, cheese, eggs, fish, liver, meat, and flour. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitamin D3 / Cholecalciferol | Vitamin/Supplement | A significant correlation exists between low levels of blood serum cholecalciferol and higher rates of various cancers, multiple sclerosis, tuberculosis, heart disease, and diabetes. Supplementation may serve a preventive role for migraine. |
| Preventive | Paid | Vitex agnus-castus | Vitamin/Supplement | Vitex agnus-castus, also called vitex, chaste tree, or chasteberry, is a shrub. It's fruit and seed are used as a herbal supplement, often to balance hormones, among other uses. Research on its benefits are limited. |
| Preventive | Free | Walking in nature | Lifestyle | A recent Stanford study has demonstrated 30 minutes of walking in nature to be as effective as an SSRI antidepressant for mild or moderate depression. As it combines exercise and stress relief, it is certainly worth trying as part of a migraine prevention strategy. |
| Acute & Preventive | Free | Wearing sunglasses | Product/Device | Glare from the sun may contribute to migraine. Ensuring you have sunglasses with sufficient UV protection and polarization to reduce glare may provide significant relief. Wear polarized sunglasses even when there is the smallest amount of sunshine if you are sensitive to sunlight. |
| Preventive | Free | Weight loss | Lifestyle | Obesity is associated with an increased risk of progression from episodic to chronic migraine. For overweight individuals, weight loss may contribute to a reduction in the frequency, severity, and duration of their migraine attacks. |
| Preventive | Paid | White willow | Vitamin/Supplement | White willow bark is an anti-inflammatory supplement that is thought to restrict prostaglandins and reduce pain. |
| Preventive | Free & Paid | Yoga | Lifestyle | A form of exercise that involves stretching, maintaining poses, and breathing control to strengthen muscles and increase blood flow. It can promote calmness and is often used in combination with meditation and breathing exercises. Yoga can be done independently or in a class under the direction of an instructor with minimal equipment aside from a mat. There are various forms of yoga including restorative, Hatha, Vinyasa, Yin, and Iyengar, among others. |
| Preventive | Paid | Zinc | Vitamin/Supplement | Zinc is needed for the proper growth and maintenance of the human body. It is found in several systems and biological reactions and it is needed for immune function, wound healing, blood clotting, thyroid function, and much more. Meat, seafood, dairy products, nuts, legumes, and whole grains offer relatively high levels of zinc. Low zinc levels have been associated with depression and diabetes among other conditions. |